Electronic Semester Blog
This is my blog for my semester notes for Interactive Art 2:Electronic Arts.
Week 2 Notes
January 17th Homework Notes
Basics of Electricity
Two Types of Electricity:
AC: alternating current
- voltage goes positive and negative
- meaured in volts (V)
- cycles per second mearues in hertz (Hz)
- power out of a wall socket/outlet
- Standard US outlet: 110V 60Hz
- Standard UK outlet: 220V 50Hz
DC: direct current
- constant voltage
- measures votage between positive and negative
- negative = 0V
- positive = voltage of current
- batteries
Ohm’s Law: V = I x R (volts = current x resistance)
Power Triangle: P / I x E (power(watts) / resistance x volts)
Multimeter can meaure volts, current and resistance
How a Breadboard Works
- Allows wires to connect while avoiding soldering
- Numbered rows are connected underneath whitin ron, not between rows
- trough in the center of board disconnects the two sides
- positive and negative colluns are conneced unerneath within the column, but not across
- sometimes disconnected halfway down board, depending on size
Flashlight Circut
Components:
- LED light
- fixed restrictors
- have specific ohms
- blue nob for variable resistance
- 0-10k ohms
When connceting positive battery, always connect last to avoid short circuting the board
Schematics and Diagrams
Has various symbols for each part
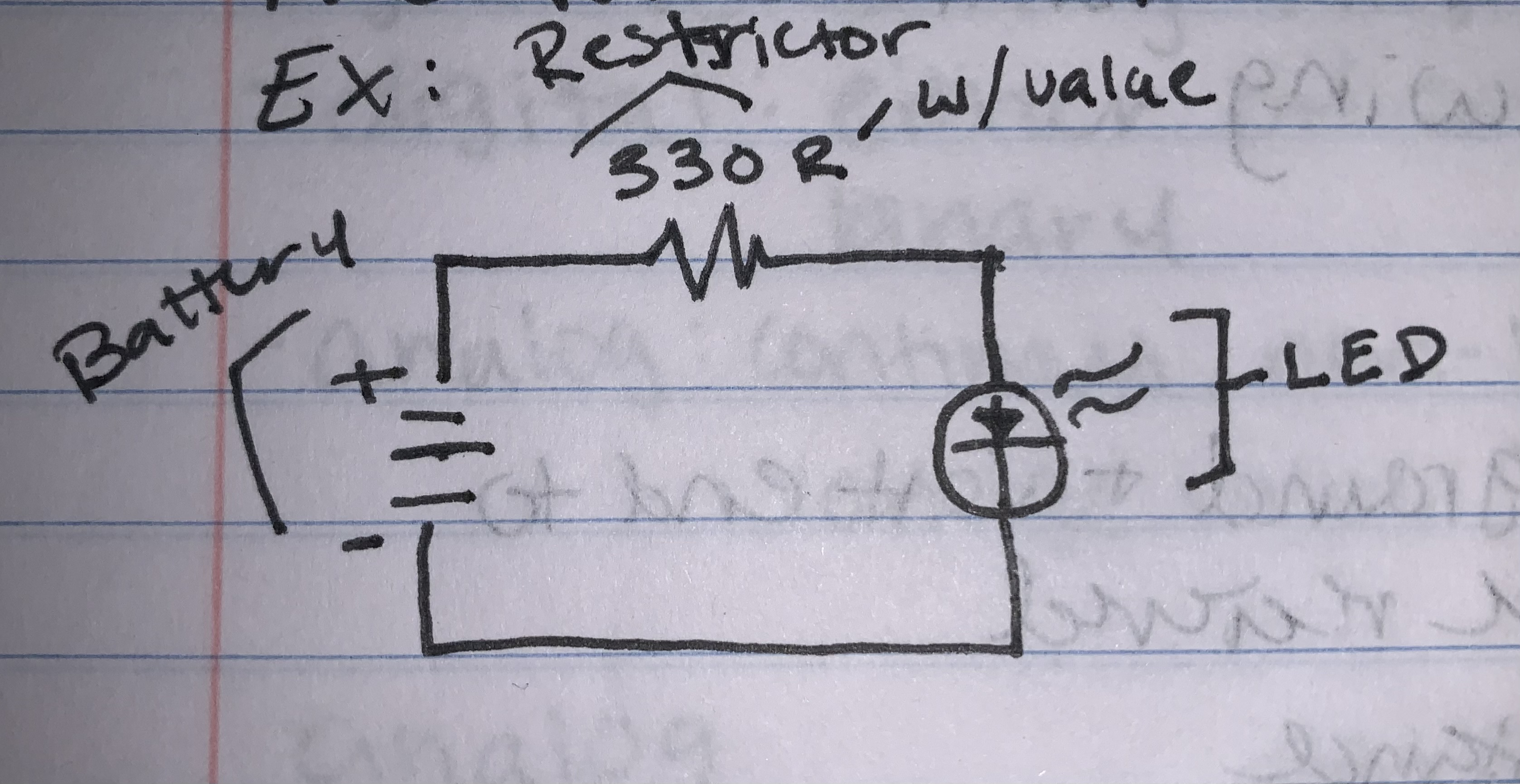
Components in a Flashlight Circut
LED
- Needs to be oriented positive/negative correctly
- inside LED bulb-
- larger wire filament = negative
- smaller wire filament = positive
- on rim of LED bulb casing- flattened edge = negative
- short leg of wire = negative
- long leg of wire = positive
- inside LED bulb-
Resistor
- non polarized - does not have positive/negative ends
- gold stripe = 5% resistance
- 3 colored striped tell ohms
- first stripe - first number
- second stripe - second number
- third stripe - number of zeros
- colors -
- black = 0
- brown = 1
- red = 2
- orange = 3
- yellow = 4
- green = 5
- blue = 6
- violet = 7
- gray = 8
- white = 9
- examples
- 10k ohms= brown/black/orange
- 10 ohms = brown/black/black
- 330 ohms = orange/orange/brown
- 1.5k ohms = brown/green/red
Lab 1
Too many volts can burn out a compontent
- Volts = pushing
- Amps = drawing
Lab 2
Voltage divider = resistors on group and volt end to change coltage recieved
Multimeter
- can measure
- DC Voltage (DCV)
- AC Voltage (ACV)
- DC Amps (DCA)
- Resistance
- com = minus (negative) input
- put dial at next highest number than the voltage
- allows most accuracy
Patentiameter = variable ohms nob
Vout = Vin x (R2 / R1 + R2)
January 18th Class Notes
IDE = Intergrade Development Environment
Platform.IO - includes a library for Arduino (requires “#include
Micro controller board - Arduino UNO
- microcontroller
- crystal
- power port
- varios pins
- Works on 5v
- others work on 3.3v
- most electronics work on 3.3v
GPIO = General Purpose Input and Output
Digital Vs Analog
- digital
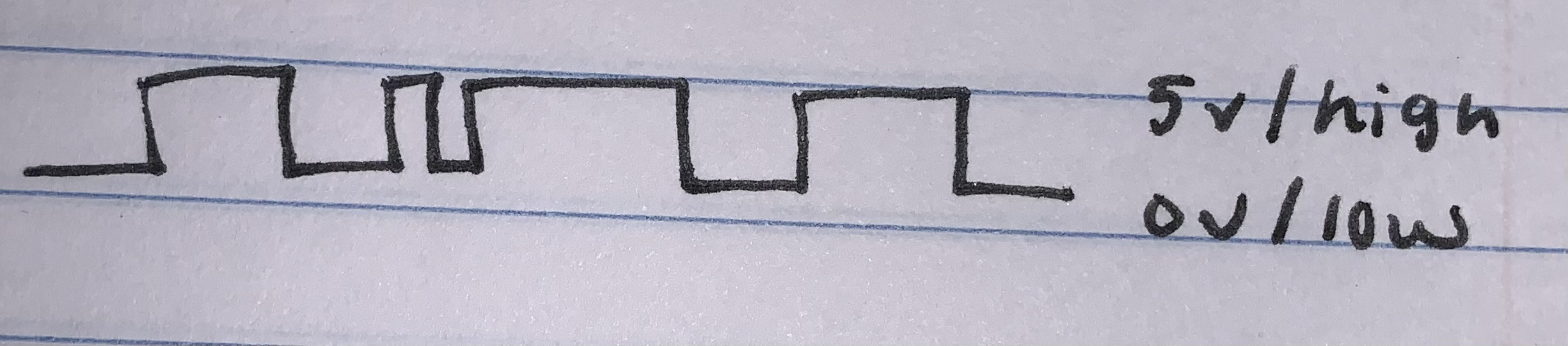
- either off or on, binary
- examples
- lamp
- cd
- files
- computer
- analog
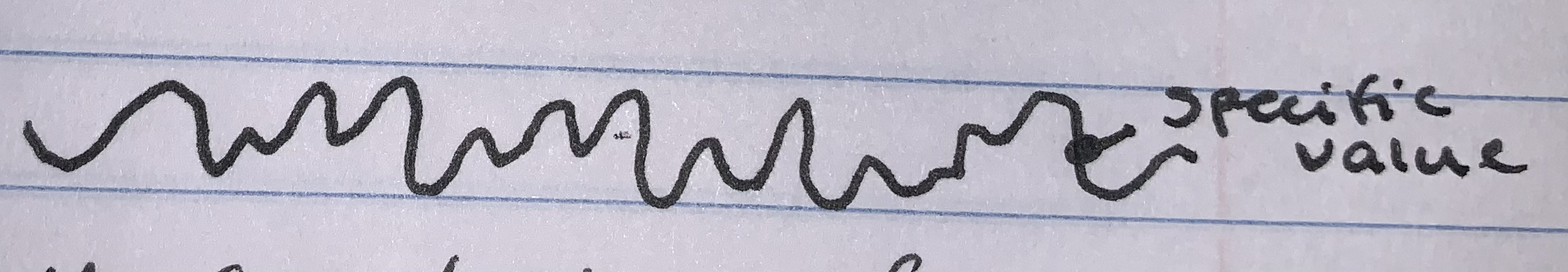
- continuous, non-binary
- voltage vaule is what we are looking for
- examples
- dimmer
- vinyl record
- wax cylinder
- DAC = digital to analog converter
- ADC = analog to digital converter
- PWM = pulse with modulation (form of DAC)
Input Examples
- Sound (mic)
- Light (sensor)
- Movement (sensor)
- Switch
- Temperature (sensor)
Output Examples
- Speaker
- Motoer
- LED/light
- LED Display
- Relay
.cpp extension = c++ file
void setup(){} = code run once
void loop(){} = code run repeatedly
- not based on cycles per amount of time, but the amount of time it takes to complete all lines in code
put pin input/output modes in setup
- pinMode(pin#,mode)
turn light on
- digitalWrite(pin#,value[high/low])
- delay(ms)
- need delay in order to have light stay on or off